Abstract
Background:
Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) is an autologous CD19-directed CAR-T-cell therapy, approved in Aug-2017 for treating children and young adults with relapsed/refractory (r/r) acute lymphoblastic leukemia and in May-2018 for treating adults with r/r diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Post-approval, a key goal has been to upscale and continuously improve manufacturing success and turnaround time in the commercial settings to meet the needs of a global patient population. Here we report accrued experience from our 4-year journey of optimizing the commercial tisagenlecleucel manufacturing process at the US site (Morris Plains, NJ), for faster and successful delivery to patients in the US.
Methods:
As reported previously, the tisagenlecleucel manufacturing process includes leukapheresis of the patient's peripheral blood mononuclear cells, enrichment and activation of T cells, transduction of the lentiviral vector containing the anti-CD19 CAR transgene, activation with anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-coated beads, expansion in cell culture, washing, and formulation of the viable cells into a cryoformulation medium. The final product is then cryopreserved, shipped back to the treatment center and infused to patients (Tyagarajan, 2020). Use of cryopreserved leukapheresis material as the starting point in commercial manufacturing is unique to tisagenlecleucel; this allows flexibility in terms of scheduling leukapheresis when a patient's health is optimal to provide T cells, and also helps offset logistical challenges (Tyagarajan, 2019).
Results:
As of Jun-2021, tisagenlecleucel has been manufactured for >5000 patients worldwide, enabled by Novartis's significantly increased global manufacturing footprint at six sites strategically located across six countries (US, France, Switzerland, Germany, Japan and Australia) and a global treatment network of >340 certified centers, including 127 centers in the US.
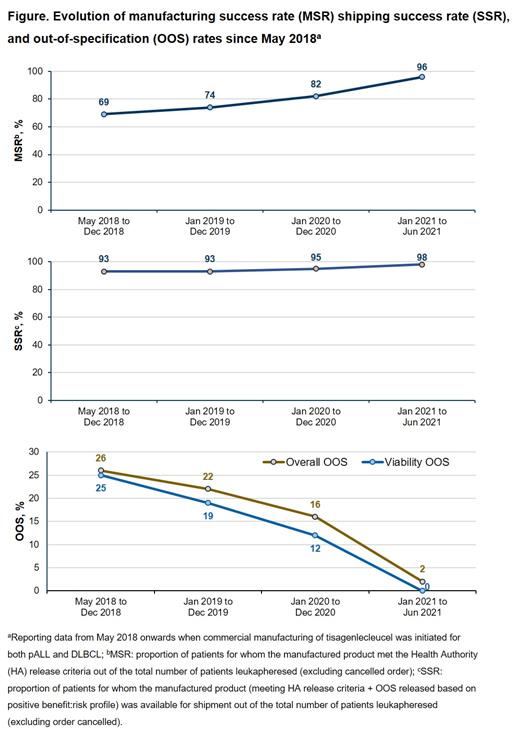
Specifically for the US manufacturing site, between Dec-2020 and Jun-2021, 376 patients in the US had starting material available for manufacturing. Overall, the manufactured product was available for shipment for 98% of patients (shipping success rate [SSR]). The commercial manufacturing success rate (MSR) was 96%, with an out-of-specification (OOS) rate of <3% and no OOS for viability. All ten OOS batches were released for infusion as benefit:risk assessment was positive. Manufacturing was cancelled for two patients upon physician's request.
Immediate manufacturing capability without waiting time was available on receipt of all apheresis starting materials. The median time from start of manufacturing to shipping was 20 days. As is evident, the COVID-19 pandemic did not appear to have significantly affected the success rate or manufacturing turnaround time.
These latest success metrics, reflecting significant improvements from 2018 to 2021 in MSR (69% to 96%), SSR (93% to 98%), and overall OOS rate (26% to 2%) including viability OOS rate (from 25% to 0%), are a result of upscaling the manufacturing capabilities, enhancements with hospitals focusing on optimizing apheresis collection and cryopreservation procedures, and continuous evaluation and improvement of the manufacturing process since tisagenlecleucel was first launched (Figure). Two key process and analytical improvements that were considered to have improved robustness of manufacturing and testing processes, reduced OOS rates, and minimized variability in turnaround time were introduced towards the end of 2020. Firstly, a simplified sample preparation procedure for final product cell count and viability measurement, which is more reflective of final product at infusion. Secondly, an alternate serum source (5% plasma-derived human AB serum [PD hABs]) which further improves process robustness with a trend towards improved growth and higher peak cell counts.
Conclusions:
Tisagenlecleucel's current global commercial manufacturing footprint and treatment network are well-positioned to meet anticipated future increase in demand for CAR-T therapies. Recent process improvements have significantly increased the MSR (to 96%) and SSR (to 98%), and immediate product availability for patients in need of CAR-T cells. Ongoing and upcoming process improvements are anticipated to further reduce the throughput time, thus allowing more patients faster access to CAR-T therapy.
Rodrigues: Novartis: Current Employment. Duran: Novartis: Current Employment. Eschgfaeller: Novartis: Current Employment. Kuzan: Novartis: Current Employment. Habucky: Novartis: Current Employment.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal